Trigger Finger Prevention and Treatment
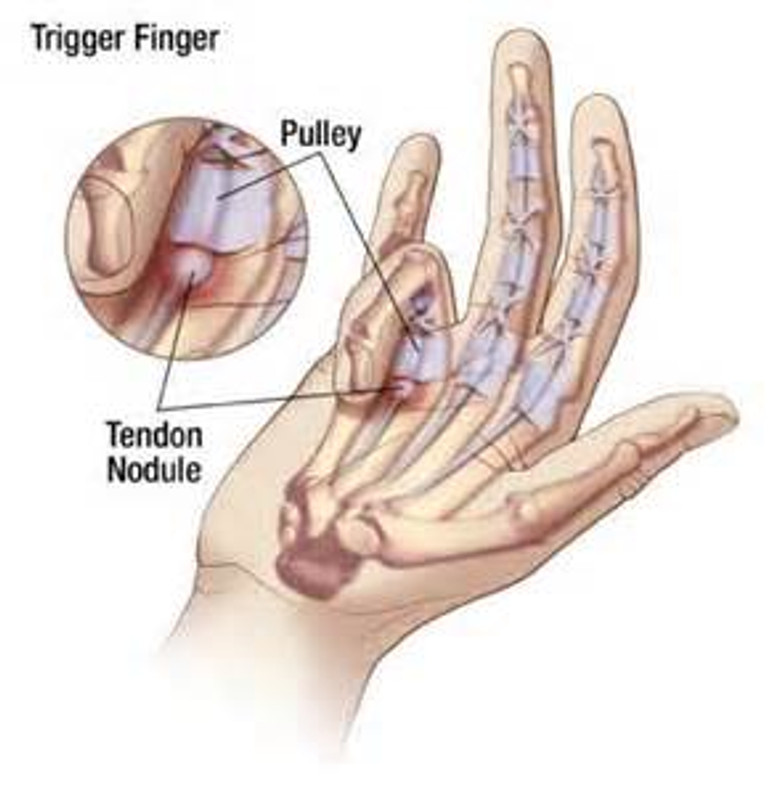
Trigger Finger, medically known as stenosing tenosynovitis, is a condition that affects the fingers, causing them to get stuck in a bent position before popping straight with a snapping sensation, resembling the pulling and releasing of a trigger. While it might seem like a minor inconvenience, if left untreated, it can lead to pain, stiffness, and even limited mobility.
What Causes Trigger Finger
The primary cause of trigger finger is the inflammation of the tendon sheath, the protective covering of the tendons that enable smooth movement of the fingers. Several factors can contribute to this inflammation, including repetitive hand and finger movements, prolonged gripping activities, certain medical conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and diabetes, and even hand injuries.
Trigger Finger Prevention
While trigger finger can sometimes develop despite precautionary measures, there are steps individuals can take to reduce their risk:
- Ergonomic Awareness: Maintain proper ergonomics when performing repetitive hand tasks. Take frequent breaks and practice stretching exercises to relieve stress on the fingers and tendons.
- Hand Exercises: Incorporate hand exercises into your daily routine to strengthen the muscles and improve flexibility. Simple exercises like finger stretches, making a fist, and using hand grippers can help.
- Avoid Repetitive Movements: Limit repetitive hand movements whenever possible. If your job involves activities like typing, sewing, or using handheld tools for extended periods, take breaks to rest your hands and stretch your fingers.
- Use Proper Technique: When engaging in activities that require gripping, ensure you're using the correct technique to minimize strain on the fingers and tendons. Avoid excessive force and maintain a relaxed grip whenever possible.
- Protective Gear: If you participate in activities that pose a risk of hand injury, such as sports or manual labor, use appropriate protective gear to reduce the likelihood of tendon damage.
Trigger Finger Treatment
If you suspect you have trigger finger or are experiencing symptoms such as finger stiffness, popping, or locking, it's essential to seek medical attention promptly. Treatment options may vary depending on the severity of the condition, but common approaches include:
- Rest and Immobilization: Resting the affected hand and avoiding activities that exacerbate symptoms can help reduce inflammation and allow the tendon sheath to heal. Immobilizing the finger with a splint may also be recommended to prevent further irritation.
- Medication: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen or naproxen can help alleviate pain and reduce inflammation associated with trigger finger.
- Physical Therapy: A physical therapist can prescribe exercises to strengthen the muscles in the hand and improve range of motion. They may also use techniques like massage and ultrasound therapy to alleviate pain and promote healing.
- Corticosteroid Injections: Injections of corticosteroids directly into the affected tendon sheath can help reduce inflammation and relieve symptoms. This treatment is often effective, although multiple injections may be necessary.
- Surgery: In cases where conservative treatments fail to provide relief, or the condition is severe, surgery may be recommended. The surgical procedure, known as trigger finger release, involves widening the affected tendon sheath to allow for smoother movement of the tendon.
Trigger finger can be a painful and frustrating condition, but with proper understanding, preventive measures, and timely treatment, its impact can be minimized. By adopting ergonomic practices, maintaining hand health, and seeking appropriate medical care when needed, individuals can effectively manage trigger finger and enjoy improved hand function and comfort. If you're experiencing symptoms of trigger finger, don't hesitate to consult a healthcare professional for evaluation and personalized treatment recommendations.
Related Blog Posts:
Preventing and Managing Gamer's Wrist
Texting and Typing: Navigating Wrist Pain in the Digital Age
Understanding De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis: Prevention and Treatment Strategies
Additional Information:
stenosing tenosynovitis (National Library of Medicine)
Trigger Finger (Mayo Clinic)
Recent Posts
-
Anatomical Models and Charts: Tools of the Trade in Healthcare
What Are Anatomical Models?Anatomical Models are three-dimensional, physical representations of vari …May 18th 2024 -
The Transformative Role of Wheelchairs in Healthcare
Wheelchairs have long been an indispensable asset in the healthcare industry, offering critical mobi …May 17th 2024 -
Understanding Durable Medical Equipment (DME)
Durable Medical Equipment (DME) refers to medical devices designed for long-term use, aiding individ …May 16th 2024